Rosacea
What is Rosacea?
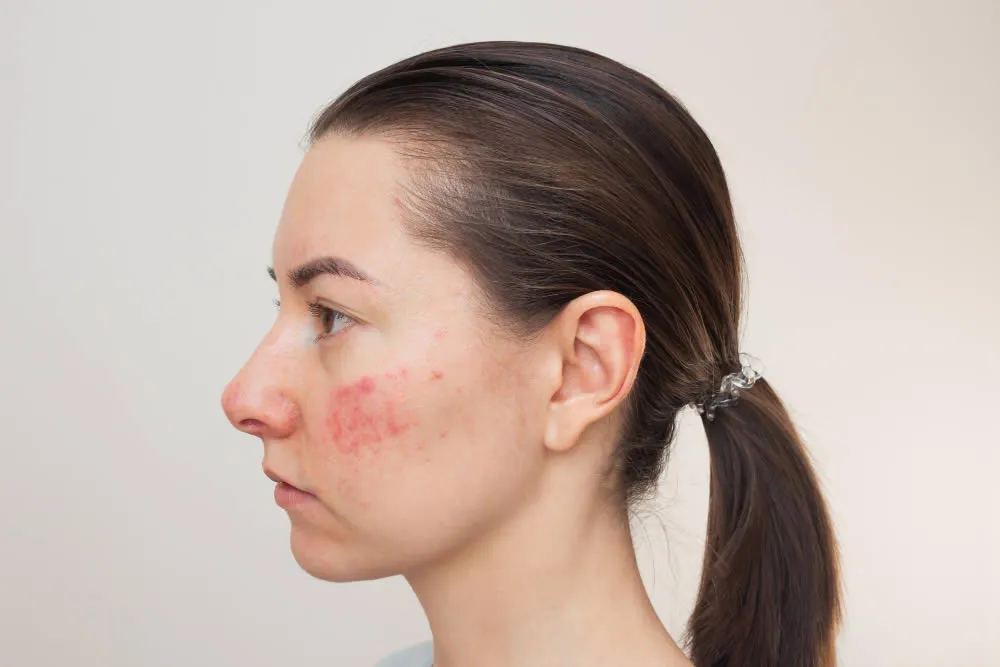
A chronic, inflammatory skin condition, rosacea affects more than 16 million Americans. Rosacea manifests itself as redness on the face that produces small, pus-filled bumps or pustules. Although rosacea is not contagious, some evidence suggests a genetic link to the condition.
Usually, most people first develop rosacea in their 30’s and then live with continuous cycles of flare-ups and dormancy. Without treatment, rosacea can have a negative impact on a person’s emotional, psychological and physical health.

What are the signs and symptoms of Rosacea?
Rosacea is a skin condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels in your face. It may also produce small, red, pus-filled bumps.
Some of the signs and symptoms of rosacea are:
- Facial blushing or flushing that comes and goes
- Visible veins on the nose and cheeks
- Swollen bumps or pimples on the face
- Burning or stinging sensation on the skin
- Eye problems such as dryness, irritation, or redness
- Enlarged nose due to excess tissue (rhinophyma)
What are the causes of Rosacea?
The exact cause of rosacea has not been identified, but the environment and genetics may play a role. If you have light skin, a family history of rosacea or experience frequent blushing, you may have an increased tendency toward developing rosacea. More women than men tend to have rosacea but men experience more severe symptoms.
Certain factors can aggravate rosacea by increasing blood flow including:
- Harsh soaps or abrasive cleanser
- Alcohol
- Corticosteroids
- Extremes in temperature
- Exposure to sun
- Hot baths and saunas
- Medications that dilate blood vessels, including certain blood pressure medications
- Spicy foods
- Stress, anger or embarrassment
- Very hot foods or beverages
- Vigorous exercise
What treatments are available at the dermatologist for Rosacea?
There are different treatments available at the dermatologist for rosacea, depending on the type and severity of your condition. Some of the treatments are:
- Topical drugs that reduce flushing, such as brimonidine (Mirvaso) and oxymetazoline (Rhofade). These drugs work by constricting blood vessels and need to be applied regularly.
- Topical drugs that help control the pimples of rosacea, such as azelaic acid (Azelex, Finacea), metronidazole (Metrogel, Noritate, others) and ivermectin (Soolantra). These drugs may take several weeks to show noticeable improvements.
- Oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline (Oracea, others), for moderate to severe rosacea with bumps and pimples. These drugs help reduce inflammation and infection.
- Oral acne drug, such as isotretinoin (Amnesteem, Claravis, others), for severe rosacea that doesn’t respond to other therapies. This drug helps clear up acnelike lesions of rosacea, but it can cause serious side effects and birth defecte.
- Laser therapy, such as pulsed dye laser (PDL) or intense pulsed light (IPL), for enlarged blood vessels and redness. These therapies use light energy to shrink the blood vessels and reduce the redness. They may cause temporary swelling and bruising.

Rosacea vs Acne
- Rosacea usually affects people older than 30, while acne is more common in teenagers and young adults.
- Rosacea only affects the face and eyes, while acne can also affect the chest, neck, back, and shoulders.
- Rosacea does not cause blackheads or whiteheads, which are typical features of acne.
- Rosacea is triggered by factors such as hot drinks, spicy foods, alcohol, temperature extremes, sunlight, wind, emotions, exercise, cosmetics, or certain medications. Acne is caused by clogged pores due to excess oil and dead skin cells.
- Rosacea has no cure, but it can be treated with medications, laser therapies, and lifestyle changes. Acne can be treated with topical and oral medications, as well as skin care products.
FAQ About Rosacea
Who is at risk for rosacea?
How is rosacea diagnosed?
What are some triggers for rosacea?
Can rosacea lead to other health problems?
How can I prevent rosacea flare-ups?
Is there a dermatologist near me in Worcester that offers treatment for rosacea?
Yes. At our Worcester dermatology office we offer treatment for rosacea to patients from Worcester and the surrounding area. Contact our office today to schedule an appointment.